Renewing its commitment to making Mazda factories globally carbon neutral by 2035, the Mazda Motor Corporation today specified important milestones on its carbon-neutrality roadmap. By Fiscal Year (FY) 2030, Mazda will reduce the CO2 emissions at its factories and operational sites in Japan*1 by 69 percent compared to FY2013 levels. To date, Mazda facilities in Japan account for 75 percent of Mazda’s CO2 emissions. Reaching this target will therefore significantly reduce Mazda’s CO2 emissions in the medium term and have a strong effect on its ability to achieve carbon neutrality.
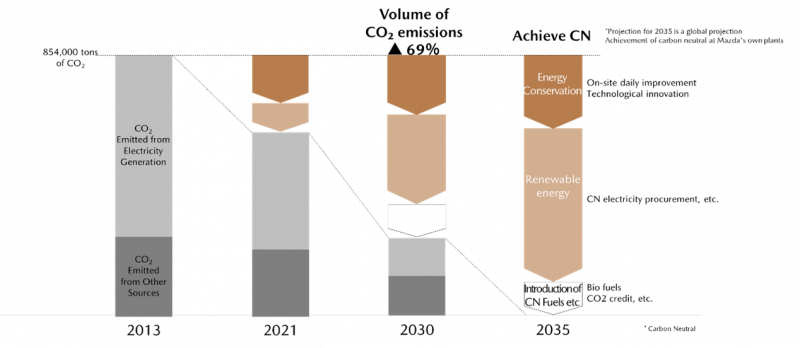
To achieve carbon neutrality at all factories globally by 2035, Mazda will be focusing on three pillars: energy conservation, shifting to renewable energy, and introducing carbon neutral fuels. Mazda announced first actions in all three areas that will be implemented domestically in the short term:
- Energy conservation
As a measure to support energy conservation, Mazda will be introducing Internal Carbon Pricing*2 as one of the capital investment criteria. As a result, investment decisions concerning Mazda facilities will consider the future price of carbon trading and prioritise investments that make a major contribution to CO2 emissions reduction. Mazda will continue working in all areas, including for example production and infrastructure, to improve the efficiency of its facilities and transform the technologies used in these areas.
- Shifting to renewable energy
Also, in Japan, Mazda will start switching the fuel used to supply the power generation facilities of MCM Energy Service Co., Ltd. (Hiroshima City, Hiroshima Prefecture), at Hiroshima plant Ujina District (Hiroshima City, Hiroshima Prefecture) from fossil fuels to liquid ammonia*3. The company will also be making use of a corporate Purchase Power Agreements (PPA)*4 signed with other local parties to increase the purchase of non-fossil fuel derived sustainable energy from power companies. As a result of these actions, Mazda plans to achieve a usage ratio for non-fossil fuel power of 75 percent by FY2030.
- Introducing carbon neutral fuels
To introduce carbon neutral fuels at its domestic facilities, Mazda will be switching the fuel used to power vehicles for transport within the company from diesel to a next-generation biofuel. In cases where generating power from alternative fuel sources proves difficult, Mazda will make use of the J-credit scheme*5 that promotes forestry preservation and re-forestry to absorb CO2 in the Chugoku region and other regions.
For this, also today, Mazda and Mitsui & Co., Ltd. have concluded a sales and purchase agreement covering J-Credits generated through appropriate forest management targeted toward the creation of a carbon-neutral society. The Credits are certified by the Japanese government under the J-Credit Scheme and will be generated through a joint project between Mitsui and a public interest incorporated association engaged in forest development in Okayama Prefecture.
Digital technologies employed in Mitsui’s Forests in Japan, including aerial surveying and satellite data, will be used to monitor forests to generate J-Credits. Some of the income provided by the Credits will be used through the joint project to develop and manage forests and enhance natural disaster preparedness. As the first company to use the Credits, Mazda will purchase credits based on the absorption of CO2 through forest conservation over an eight-year period from fiscal 2022 to fiscal 2029.
Commenting on this announcement, Takeshi Mukai, Director and Senior Managing Executive Officer (Oversight of Quality, Purchasing, Production, Business Logistics and Carbon Neutrality; Assistant to the Officer overseeing Cost Innovation), said:
“Mazda will move forward with carbon neutral initiatives in line with our plans to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions and the prevention of global warming across all of our processes including manufacturing transportation, usage, and recycling/disposal, as we believe that such efforts are a core responsibility of automotive manufacturers. Through these three pillars, Mazda is aiming to achieve carbon neutral at all of its global plants by 2035 and will attempt to achieve carbon neutral throughout the entire supply chain by 2050, contributing to the lasting coexistence with our planet.“
For factories outside Japan, Mazda will be investigating optimal approaches for each region, using the carbon neutral initiatives established in Japan as a reference model.
Major Initiatives
| Approach | Major initiatives contributing to the achievement of our medium-term goal for FY2030 (Scope1-2*6) | |
| Energy Conservation | Mazda is working steadily to achieve improvements in all of these areas, including production and indirect departments such as infrastructure | – Accelerating facilities investment through the introduction of Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP) – Improve productivity and operational efficiency (greater productivity, improved quality, improved operations, feasibility simulations, etc.) – Improve efficiency of our facilities (switch lights to LEDs, introduce inverter control into motor-driven facilities, improve efficiency of air conditioning units etc.) – Technical innovation (improve efficiency of paint spraying process, reduce temperature of heat treatment furnace etc.) |
| Introduce renewable energy | Achieve decarbonization of power generation within our plants, and procure power from third parties | – Switch fuel for Hiroshima plant’s power source from coal to liquid ammonia*3 – Make use of corporate PPA*4 concluded with local parties in each region – Purchase renewable energy and other non-fossil fuel derived energy from power companies |
| Introduce carbon neutral energy | Introduce carbon neutral fuel for in-company transportation needsMake use of CO2 credits, etc. | – Switch fuel used for in-company transportation to next-generation biofuel*7, etc. – Acquire J-credits generated in the Chugoku region (forestry CO2 absorption)*5 |
###
*1 Total of 17 places of operation in Japan including headquarters and Hiroshima plant, (Aki-gun and Hiroshima City in Hiroshima Prefecture), Hofu plant (Hofu City, Yamaguchi Prefecture) and Miyoshi office (Miyoshi City, Hiroshima Prefecture).
*2 Mazda will use internal carbon pricing to create frameworks for promoting low carbon investment and low carbon policies.
*3 Refers to power generation based solely on the combustion of liquid ammonia. Mazda has already established a collaborative body for promoting the introduction and use of ammonia fuel delivered via the Namikata Terminal (announced on April 14, 2023). Mazda has already taken part in a meeting of the new body.
*4 An agreement for the purchase of electric power over the long-term under which a power generation company establishes, for supply to a specific user, solar power facilities or other facilities, located at a distance from the user, to generate sustainable energy which is supplied to the user via the power grid of a specific power retailer. Mazda has concluded offsite corporate PPA contracts for the supply of solar power (announced on March 27, 2023).
*5 A system recognized by the Japanese government under which the introduction of energy-conserving facilities and the use of renewable energy to reduce CO2 emissions and credit for the absorption of CO2 through forestry management plans can be counted as a contribution to the goals of the Japan Business Federation’s carbon neutral action plan and carbon offsets. Mazda has already concluded with Mitsui & Co., Ltd. a contract to purchase the J Credits generated by the Okayamanomori seibikousha Forestry Management Project (announced on December 14, 2023).
*6 Scope 1: Direct emissions from the use of fuel and industrial processes.
Scope 2: Emissions resulting from a company’s purchase of heat and power (indirect emissions from energy sources).
*7 Mazda supports the biofuel manufacturing business of Euglena Co., Ltd. (announced on January 19, 2023).
(Reference)
FY2022
(FY2022 Ratio of energy supplied to headquarters and Hiroshima plant from MCM: 56% = Headquarters MCM: 364/ Mazda’s plants and operational sites: 648)
FY2022
Mazda’s plants and operational sites in Japan energy usage: 578GWh
MCM Energy Service Co., Ltd. supply of power to Mazda headquarters and Hiroshima plant: 270GWh
(FY2022 Ratio of energy supplied to headquarters and Hiroshima plant from MCM: 47% = Headquarters MCM: 270/ Mazda’s plants and operational sites: 578)




